





 Organization
Interaction
Facilitation
Materials
Instructional
Organization
Interaction
Facilitation
Materials
InstructionalStrategies Assessment

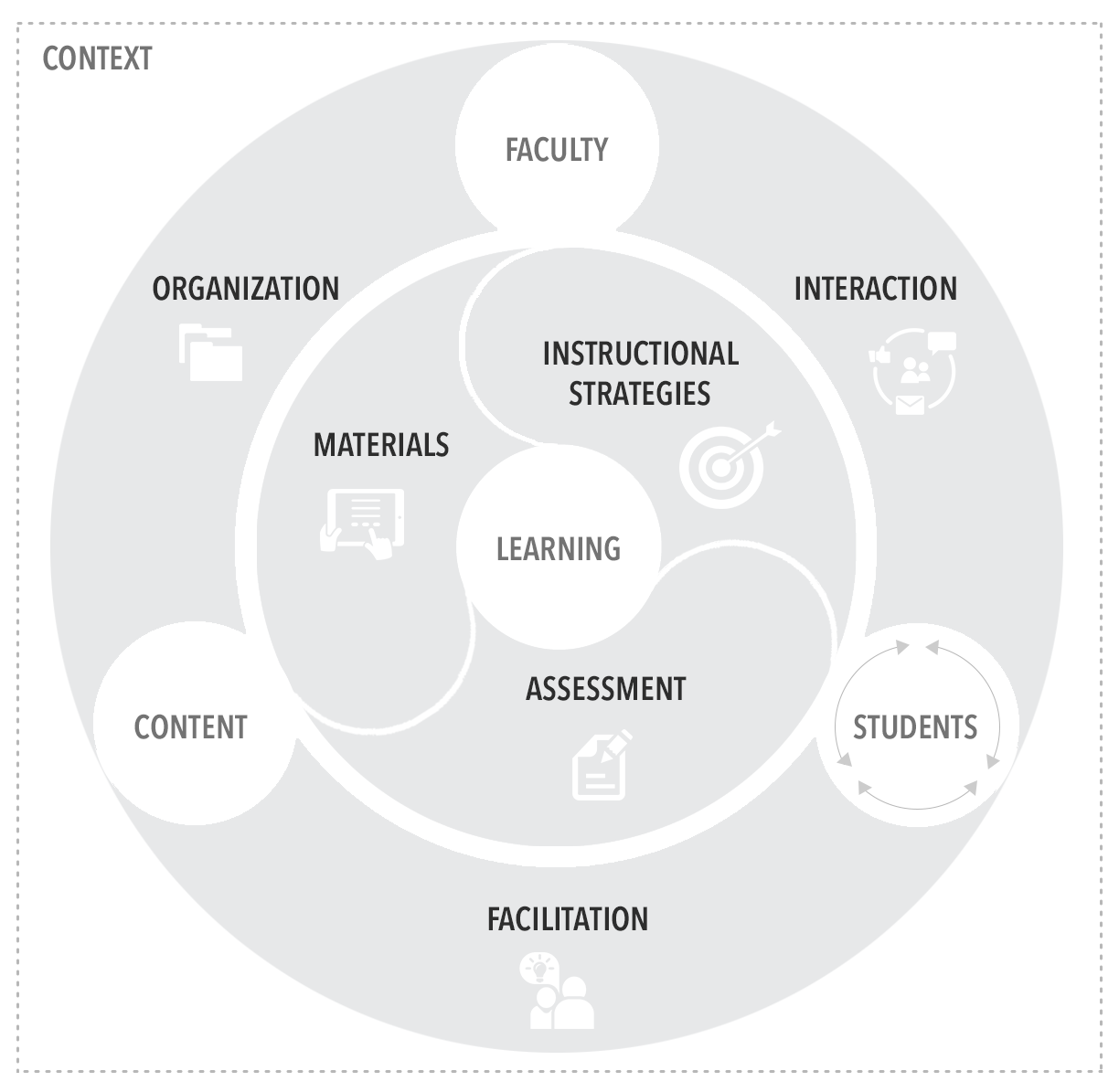
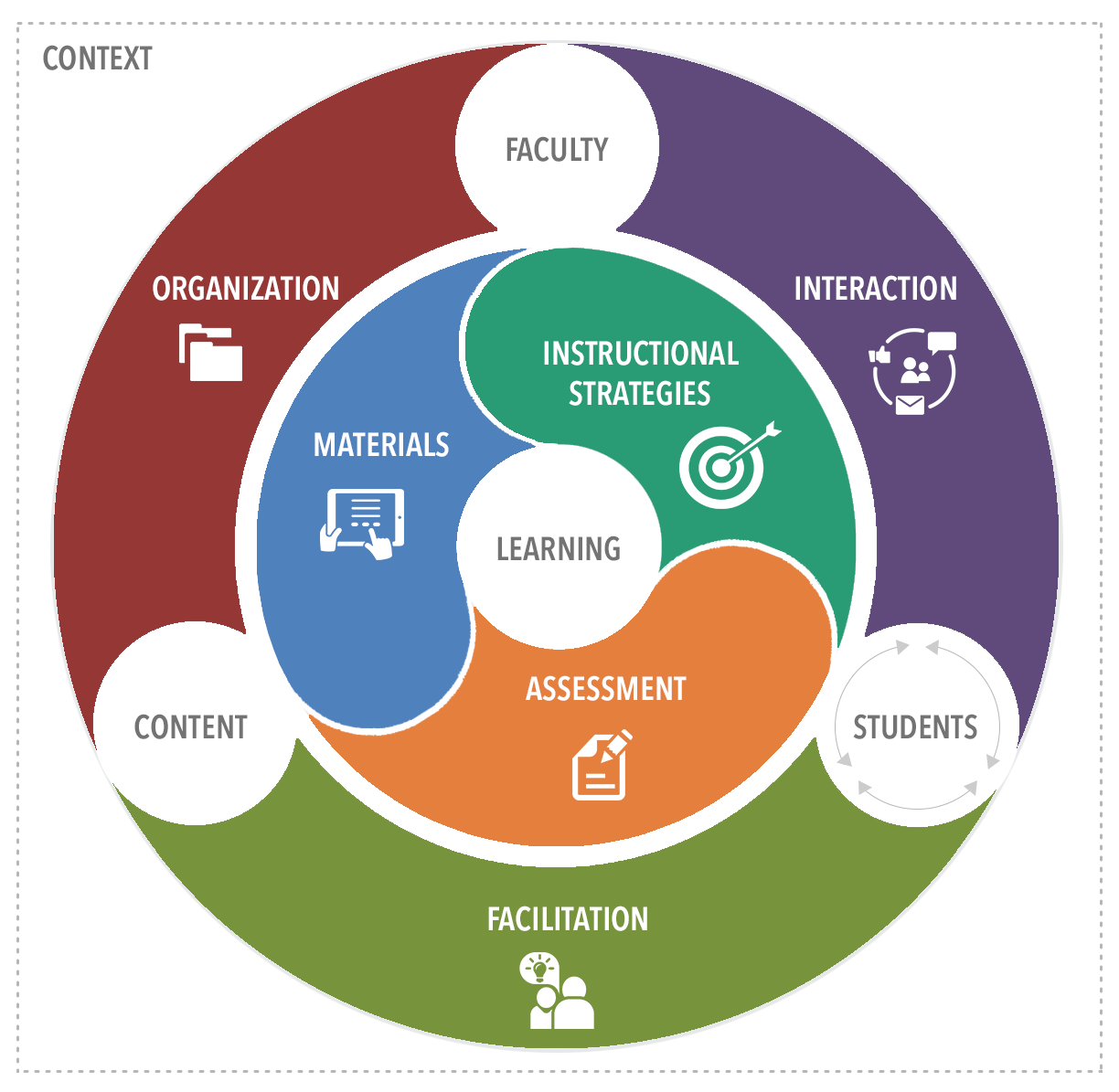
Quality of Online Education (QOE) framework
The College of Education’s QOE framework represents the interrelated actions among three main agencies (i.e., faculty, students, and content) in online education environments to facilitate faculty’s implementation of quality online courses.
Features
- It focuses on inter-relations among three agencies (i.e., faculty, students, and content) that play important roles in online education.
- It provides a systematic approach to the interdependent nature of online environments with a graphical representation.
Agency –Action –Component (What-is) –Method (How-to) - It provides various practice examples for our college’s instructors.
- It emphasizes the importance of context (e.g., discipline, students, setting, or system) that affects learning goals and activities in online courses.

ORGANIZATION (Faculty – Content)
refers to faculty’s effort to organize an online course for effective communication of learning expectation, content, and learning process.
- Organize an online course in a consistent and structured manner to minimize cognitive overload in navigating the course site.
- Design an online course compliant with ADA guidelines to provide easy access to all learners.
- Design an online course that explicitly aligns course objectives, learning activities, and assessments to clarify learning process and expectations.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Course home page |
|
| Course orientation |
|
| Menus (navigation) |
|
| Syllabus |
|
| Schedule page |
|
| Module page |
|
| ADA compliance |
|

INTERACTION (Faculty – Students)
refers to faculty’s effort to build a community for students to share perspectives and interests and collaborate on tasks.
- Help students have a sense of community to support each other’s learning process.
- Build a safe learning environment for open discussions with the instructor and peers.
- Sequence learning content in an increasing order of difficulty to help students deepen their interactions with content.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Welcome message & Self-introduction |
|
| Student-Instructor interaction |
|
| Student-Student interaction |
|
| Student-Content interaction |
|
FACILITATION (Content – Students)
refers to faculty’s continuous monitoring and scaffolding to improve student learning.
- Monitor students’ learning progress to keep them on track.
- Provide constructive feedback in a timely manner to improve student performance.
- Design routines to support students’ proactive self-regulated learning.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Scaffolding |
|
| Feedback |
|
| Monitoring |
|
| Institutional support |
|

MATERIALS (Faculty – Students - Content)
refers to faculty’s creation and presentation of accurate, current, and relevant contents to increase students’ interest in learning new knowledge.
- Provide up-to-date course contents to introduce current trends and issues in the field.
- Use various forms of media to effectively deliver important messages.
- Provide relevant learning materials to increase student motivation.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Learing contents |
|
| Assignment material |
|
| Supplementary material |
|
| Copyright and fair use |
|
| ADA compliance |
|

INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES (Faculty – Students - Content)
refers to faculty’s approaches and means to engage students for deeper learning.
- Apply effective strategies to promote students’ content mastery.
- Assign authentic tasks to foster active participation in the learning process.
- Incorporate guided practice to help students apply and transfer knowledge and skills.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Instruction |
|
| Activities |
|

ASSESSMENT (Faculty – Students - Content)
refers to faculty’s design and use of various methods for assessment to ensure students’ achievement of learning objectives.
- Assess regularly student performance to ensure students meet the intended learning outcomes.
- Use of various types of methods to effectively assess learning progress.
- Provide clear instructions, evaluation criteria, and constructive feedback to foster improvements in learning.
COMPONENT (WHAT-IS) METHOD (HOW-TO)
| Formative assessment |
|
| Summative assessment |
|
| Guidelines |
|
| Criteria |
|

